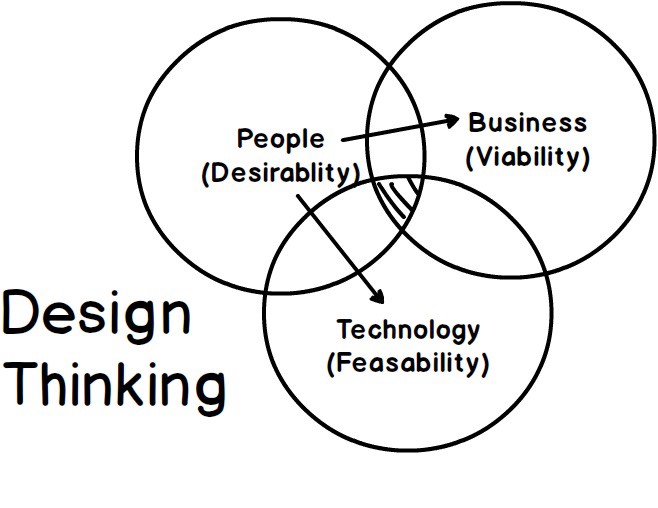
This article summarizes learnings from Kellogg’s Design Thinking workshop and pulls together various resources and articles on the subject. After graduating the eMBA program from Kellogg in 2005 I have been involved in many aspects of user experience and this workshop brought it all together. Design Thinking is about applying the (design) process of designing physical products to business decisions, services and even process improvement initiatives.
We had the honor to have one of our Kellogg alumni colleagues, David Schonthal, also a Business Designer at IDEO, guide us through the course.
The curriculum included hands-on experience in brainstorming and developing prototypes of our ideas at the all inspiring IDEO office in downtown Chicago and guest speaker Bob Moesta. If there is one thing you get from this blog post it is you must prototype! Best said by David Kelley, Founder of IDEO:
The 3 basic steps of Design Thinking:
1. Learn about the world (research)
2. Have some ideas (brainstorming)
3. Make the ideas real (prototyping)
1. Learn about the world:
The Design Thinking begins with the users
- Observe human behavior
- Changing behavior is difficult and expensive — you might want to be inspired by what people are already doing (Bank of America — Keep the change initiative: People round up their checks to get ahead)
- Look in similiar places: Emergency room — Formula One car race pit
- Understand the jobs to be done (JTBD).
4.1 Clayton Christensen, professor at Harvard Business School:
Innovator’s toolkit:
4.3 Bob Moesta: Understanding the Jobs to be Done
5. Consider the journey of the users:
6. Look at extreme users:
Courtesy of Slides from Kellogg Presentation
7. Live in context of the user
8. Combine context with empathy: be the user, wear the briefs, eat your own dog food!
2. Have some ideas (brainstorming)
Brainstorming is a method to generate ideas. Lot’s of ideas, crazy ideas too! Think outside of the box. Here are some general brainstorming guidelines:
After the brainstorm you want to organize and synthesise your ideas to identify the one’s that go to the next step: prototyping
3. Make ideas real — build prototypes
Prototypes embodies questions! “The scrappier the better!” Anything can be prototyped by using different tools:
1. Services: create a kid experience at Chipotle. (Example prototype: kids can’t read the menu, provide food selection experience with “plastic” food during the waiting period to be used as the order.)
2. Experiences
3. Environments
4. Interactions and Interfaces
Here is an example of a first prototype of a mobile game:
Here is what it ends up being:
5. Business Models (check out the Business Model Canvas at:)
Strategyzer |Business Model Generation
Business Model Generationbusinessmodelgeneration.com